Return on Equity ROE: Formula, Calculation, and Use Cases
This shows that the company is using a mix of equity and debt to finance its assets. When analyzing the equity multiplier, it is essential to consider how it varies across different industries and companies. This comparison provides valuable insights into the financial health and leverage strategies employed by businesses. Let’s explore the significance of comparing equity multipliers and how it can help in making informed investment decisions. For example, if a company has total assets of $1,000,000 and total equity of $500,000, the equity multiplier would be 2 ($1,000,000 / $500,000). This means that for every dollar of equity, the company has $2 of assets.
Profit Margin
- If the ratio is high, it implies that the company uses a higher amount of debt to finance its assets.
- However, always assess this in the context of the industry and business model.
- This comparison provides valuable insights into the financial health and leverage strategies employed by businesses.
- If a company has a high equity multiplier, it borrows to finance purchases, so its debt burden is higher.
- It can justify borrowing because its revenues grew by an average of just over 11% a year between 2018 and 2021, much higher than the interest rate charged by lenders.
For example, if a company has $2 million in total assets and $1 million in shareholders’ equity, its equity multiplier would be 2 ($2 million / $1 million). This suggests the company is using a significant amount of debt financing to fund asset growth. The equity multiplier is a relevant factor in the DuPont analysis which is a method of financial analysis that was devised by the chemical company for its internal financial review. The DuPont model breaks the return on equity (ROE) calculation into three ratios; asset turnover ratio, net profit margin, and equity multiplier. The equity multiplier is a key component of the DuPont Analysis, which breaks down return on equity (ROE) into profit margin, asset turnover, formula for equity multiplier and financial leverage. The equity multiplier represents the financial leverage component, helping analysts identify how leverage affects shareholder returns.
- Well, for every dollar of assets A&B Wears owns, about 33 cents are financed by equity.
- In the case of Company C, an automotive manufacturer, the equity multiplier has steadily increased over the past five years.
- Companies can issue two types of stocks – ordinary stocks and preferred stocks.
- There is no ideal value for an equity multiplier ratio because not all business strategies are the same.
Significance and Use of Equity Multiplier Formula
A business with a high equity multiplier has a high level of liabilities (including debt) relative to its equity and is said to be highly leveraged. As liabilities need to be repaid before equity, a highly leveraged business is considered to be more risky for the owners and investors. The balance sheet below is used as an example to show how to calculate the equity multiplier ratio.
- This is because if the cost with the interest paid on loans and debts is low or tends to zero specialists recommend to rely on debts to develop a business either new or a established one.
- This means that for every dollar of equity, the company has $2.50 in assets, implying that $1.50 is financed by debt.
- Here are examples to illustrate the equity multiplier across different company scenarios.
- This is the case if the company finds it is cheaper to incur debt as a financing method compared to issuing stock.
- But there are industries that allow for much higher equity multipliers (10 and above).
The Role of the Equity Multiplier in the DuPont Analysis
- The asset turnover ratio is another key financial ratio that provides insight into a company’s efficiency in using its assets to generate revenue.
- In a good equity multiplier if the Assets To Shareholder Equity is higher, the ROE under DuPont analysis will also be higher.
- Some companies strategically use debt to fuel growth and may operate successfully with a higher equity multiplier.
- When a company’s equity multiplier is low, it shows that a company a generally financed by stockholders, so debt financing is low and the investment is fairly conservative.
A high ratio indicates reliance on debt financing and highlights liquidity risk if cash flows decline. A higher equity multiplier ratio generally means a company is relying more heavily on debt financing relative to equity financing. In summary, the equity multiplier is a useful metric for assessing financial risk and analyzing how profitable a company is relative to shareholder investments. Understanding this formula can provide helpful insight into a company’s financial leverage, efficiency, and value creation ability.
Interpreting High vs. Low Ratios

The equity multiplier is one of the ratios that make up the DuPont analysis, which is a framework to calculate the return on equity (ROE) of companies. To explain leverage analysis, we use the example of Apple Inc. and Verizon Communications Inc. In March 2016, Apple’s total assets stood at $305 billion, while the value of the shareholder’s equity stood at $130 billion. When you compare these examples, it’s evident that the equity multiplier is not just a number but a reflection of an industry’s characteristics and a company’s strategic financial choices. Investors should analyze the equity multiplier in conjunction with other financial indicators and the company’s industry, management practices, and market conditions to make informed decisions.
A lower equity multiplier ratio may indicate a lower risk profile for Walmart compared to companies with higher ratios. Exxon Mobil’s equity multiplier ratio of 2.37x suggests that the company uses a more balanced approach to financing its assets, with a higher proportion of equity compared to debt. Apple’s high equity multiplier ratio of 5.57x indicates that the company relies heavily on debt financing to fund its assets. This could expose Apple to higher financial risk if it faces difficulties in generating sufficient cash flows to service its debt obligations.
Calculating the Debt Ratio Using the Equity Multiplier
On the other hand, the ratio also indicates how much debt financing is being used for asset acquisitions and day-to-day operations. This company only used 20% debt to finance its assets, that is 1,000,000 – 800,000 / 1,000,000 x 100. Therefore, the financing structure of the company is conservative and with this, creditors will be willing to advance debt to it. The equity multiplier and the debt ratio, although both being important financial ratios, serve different functions when it comes to financial analysis. Both ratios revolve around the idea of assessing a company’s financial leverage.
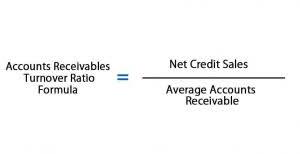
Implications of Equity Multiplier in Risk Management
A low equity multiplier implies a relatively small amount of debt (as the share of assets financed by shareholders’ equity is relatively high). Conversely, a high ratio suggests a relatively high amount of debt (since the share of assets financed by shareholders’ equity is relatively low). We calculate the equity multiplier as average total assets divided by average total Mental Health Billing equity. Some companies strategically use debt to fuel growth and may operate successfully with a higher equity multiplier.

A high use of debt can be part of an effective business strategy that allows the company to purchase assets at a lower cost. This is the case if the company finds it is https://internationalvalvebuyers.com/mastering-hoa-accounting-a-beginner-s-guide-to-2/ cheaper to incur debt as a financing method compared to issuing stock. Comparing equity multipliers in this manner enables assessing relative risk-reward profiles across investment options. It also contextualizes capital structure decisions specific to certain industries.
